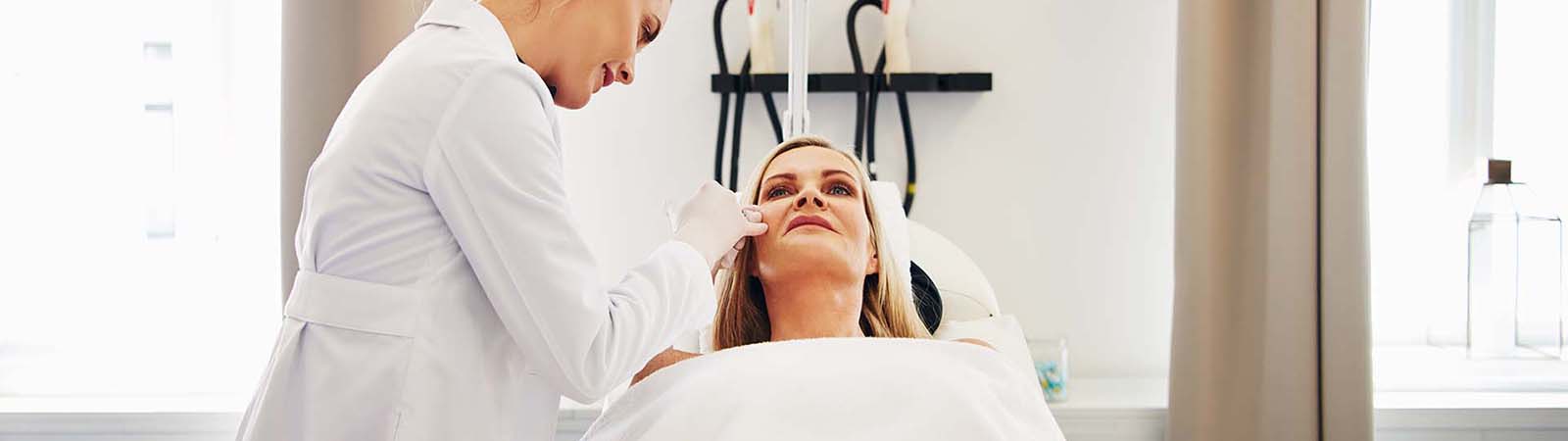
Botox is a protein derived from Botulinum toxin, which is produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. When doctors utilize this medicine cautiously, appropriately, and in tiny doses, it can provide a wide range of advantages that people nowadays desire and demand. Botox is a medication that has both aesthetic and medicinal applications and advantages. Botox injections, as a cosmetic therapy, can minimize the sight of skin wrinkles or lines and make the skin look and feel smoother. Below is an explanation of how Botox works, as well as its applications, the process of injecting Botox, and other important information that you should be aware about.
What is Botox?
Botox is derived from the C. botulinum bacterium, which may be found in a variety of natural environments, including soil, lakes, woods, and the digestive systems of animals and fish. C. botulinum bacteria and spores that occur naturally are typically harmless and do not pose any dangers. When the spores change and the cell population grows to a particular size, the bacteria starts manufacturing Botulinum toxin, a neurotoxin that causes botulism.
Botox is safe to use and delivers a variety of advantages when used correctly in a therapeutic environment and does not reach the stage of botulism. Botox injections are made using extremely tiny amounts of Botulinum toxin. The medicine has the ability to temporarily immobilize muscles, which can help persons with a variety of muscular or nerve diseases. Some commercial preparations of Botulinum toxin are onabotulinumtoxin A (Botox), abobotulinumtoxin A (Dysport), incobotulinumtoxin A (Xeomin), rimabotulinumtoxin B (Myobloc) and prabotulinumtoxin A (Jeuveau). The term, “Botox”, is used by the general public to describe these products together.
How Botox Works
Botox contains a neurotoxin that is used with care and caution. These toxins attack the neurological system, interfering with the nerve signaling pathways that cause muscular contraction. This is how the medication temporarily paralyzes the muscles surrounding the injection area. The neurons produce a chemical message called acetylcholine at the intersection where nerve terminals meet muscle cells in order for any muscle tissue to contract. Acetylcholine binds to receptors on muscle cells, causing them to contract or shorten. Botox injections block the release of acetylcholine, which causes muscle cells to contract. In this way, the toxin aids in the relaxation of the muscles.
Procedure
Botulinum toxin is administered to patients by dissolving the powder in saline and inserting it straight into neuromuscular tissue. The chemical takes 24-72 hours to take action and it is possible that the full benefits will take up to 5 days to manifest. They can persist anywhere from 3 to 12 months, depending on the therapy and what you do to take care of the injection area, as well as your body as a whole. Botox should be avoided during pregnancy and nursing, as well as if you have ever had an adverse response to the medicine or any of its constituents. If there are any other concerns or confusions that you may have, discuss them with a doctor.
Cosmetic Uses
Botox is primarily used to reduce the appearance and development of facial wrinkles. According to several surveys, Botox injections are the most popular cosmetic surgery in the United States, and countless people have gotten Botox treatments in recent years. The benefits are transient, lasting between 3 and 12 months depending on the level of therapy. People frequently seek injections in areas such as the frown lines, glabellar lines, or elevens between the brows, the crow’s feet around the eyes, the horizontal folds in the forehead, lines at the sides of the lips, and “cobblestone” skin on the chin. Some people also use Botox to improve the look of their hair.
Medical Uses
Botox is also used by healthcare experts to treat a range of medical disorders, the majority of which involve the neuromuscular system. Botox is used for the following applications: upper limb spasms in those older than 2 years, misaligned eyes or strabismus in those older than 12 years, extreme underarm perspiration or hyperhidrosis, and migraines or headaches lasting at least 4 hours on 15 or more days per month are the some of the disorders treated with Botox.
Other conditions that this treatment can affect are symptoms of an overactive bladder caused by a neurological illness that anticholinergic medications cannot fix, eyelid twitches or blepharospasm caused by dystonia, and a neurological disorder termed cervical dystonia that deals with the head and causes neck aches. Botox injections are also used for off-label, or unapproved purposes, such as treating alopecia, sialorrhea (excess saliva production), psoriasis, and dyshidrotic eczema (inflammation of the palms and soles of the feet).
Botox is also used to treat anismus (weakness of the anal muscle), post-herpetic neuralgia vulvodynia, (pain and irritation in the vagina), and achalasia (a throat problem that makes swallowing hard to perform).
Other Potential Uses
Other problems and health conditions that may benefit from off-label Botox usages, according to existing evidence, include face discolouration and flushing, including during menstruation, keloids and scars from tissue regeneration, hidradenitis suppurativa (an inflammatory skin disease), and blistering sores caused by Hailey-Hailey. Even though these conditions can potentially be treated with Botox , further study is needed to demonstrate that Botox is safe and consistently effective for off-label treatments like these. Scientists must also determine the optimum means to provide medicine in each situation, so it is preferable to seek alternatives before settling on this one.
Using Botox, doctors will be able to temporarily immobilize muscles that tend to contract. Because of this, Botox is a commonly used injection that primarily treats wrinkles and roughness on the skin, most especially on the face. There are other various cosmetic and medical uses that Botox is known for, like sweating disorders, muscle spasms, migraines and face discolouration, just to name a few. For this drug, it takes between one and three days for the benefits to kick in and five days for it to reach its full potential. Additionally, the benefits provided by this treatment lasts anywhere between 3 to 12 months, depending on the type of treatment and how well you take care of your skin and body. If you have any further questions about Botox, speak to a local doctor today.